Window Glass:
Energy Saving Options
- GOAL:
- The student will understand the importance of using different types of glass in order to increase energy efficiency.
- OBJECTIVES:
- The student will be able to:
- 1. Explain heat losses and gains through glass.
- 2. Describe types of glass and windows that can increase a home's energy efficiency.
- LESSON / INFORMATION:
- Many people enjoy the windows on their home for the lighting, ventilation, and view they provide. They do not realize that having many windows also has disadvantages.
- Can you think of three disadvantages of having many windows?
- _______________________________________________
- _______________________________________________
- _______________________________________________
- Windows are now recognized as "thermal weak spots" in a house. Up to 15 times more heat is lost or gained through windows as is lost or gained through an equal area of wall space.
- Unprotected, 1/8" windows can account for up to 25% of heat lost during the winter and of heat gained during the summer. There are ways, however, to increase the energy efficiency of windows.
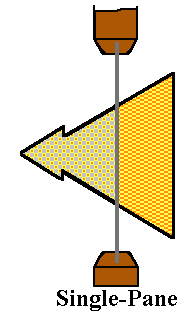
- Multiple Glazings -
- One important way to decrease energy loss through windows is to increase the number of panes, or glazings.
- A single-paned, untreated window unit is very energy inefficient. A measurement of its resistance to heat shows that this single paned window has a value of about R-1. A double-paned, untreated unit has a rating of R-2.1, and a triple paned unit has a value of R-3.2.
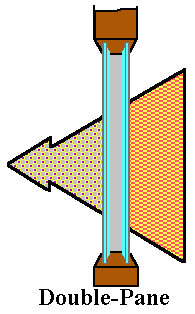
- Thus the energy efficiency of a window can be more than tripled by using triple paned instead of single-paned glass. This insulating effect is created by the air spaces found between the panes of the window. These air spaces reduce heat losses and gains through the window.
- Additional panes in the window unit, however, do increase the cost and the weight of the unit.
- Low-E Glass -
- While adding additional panes of untreated glass does increase the energy efficiency of window, putting a special coating on the windows also increases its window insulating capacity.
- One type of specially coated glass is low-e, or low emittance, glass. This treatment is only used on double paned windows and the coating is on a surface that faces the air space.
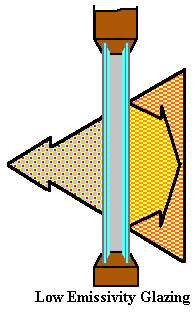
- In warm regions like Louisiana, the coating should be on the enclosed surface of the outside pane. This causes heat to be reflected away from the house.
-
- Double paned windows with the low-e glaze are 35% more energy efficient than untreated double-paned windows. The R-value of these windows varies from R-2.5 to R-3.5. As the R-values of these windows increase so does the cost.
- Gas-Filled, Low-E Windows -
- Some companies fill the airspace in low-e windows with argon gas instead of air. This gas is safe, inexpensive, and readily available. Argon is used because it is an inert gas that does not transfer heat as well as air.
- If it is not possible to use multiple paned windows or low-e glass, what are some other ways to prevent energy loss through windows? Check off the 5 options below that you think are most helpful in reducing heat losses and gains through windows.
- _____Shade window with trees or shrubs
- _____Shade window with roof overhang
- _____Use solar screens instead of regular insect screens
- _____Use storm windows
- _____Put a form of tinting on the outside of the window
- _____Opaque window shades
- _____Mini-blinds
- _____Insulated curtains
- _____Window drapes
- _____Venetian blinds
- RECOMMENDED READING:
- Window Innovations, Conservation and Renewable Energy Inquiry and Referral Service, (ED-). Silver Spring, MD, 1990.
- Building Energy Efficient Homes in Louisiana. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources, Baton Rouge, LA, n.d.
- Using Passive Solar Concepts in Louisiana. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources, Baton Rouge, LA, n.d.
- Low-E Glass: It's the Latest Technology in Windows. SLEMCO, Lafayette, LA, n.d.
- INFORMATION CHECK
- Place a "T" in front of statements that are true and an "F" in front of statements that are false. Beneath each false statement, explain why it is false.
- _____1. Windows are an asset as they provide lighting, ventilation, and a view of the outdoors.
- _____2. Windows are now recognized as "thermal strong points" since very little heat is lost or gained through them.
- _____3. Unprotected 1/8" glass can account for up to 50% of heat loss in the winter and for 75% of heat gains in the summer.
- _____4. Windows are not very energy efficient. All you can do about this is to have very few windows on the house.
- _____5. Going from a single pane to a double pane window doubles the heat resistance of that window unit.
- _____6. The insulator in double paned windows is air.
- _____7. Low-e glass refers to glass with a low energy efficiency rating.
- _____8. The special coating used in low emittance glass must be used on the inside of double paned, sealed windows.
- _____9. To keep heat out, the low emittance coating must be on the enclosed surface of the inside pane.
- _____10. Windows with low-e glass are about 35% more energy efficient than regular double-paned windows.
- _____11. Low-e glass helps save energy but is so expensive that the regular homeowner cannot afford it.
- _____12. Some low-e windows are filled with neon instead of air.
- _____13. Some low-e windows are filled with gas because the gas acts as a coolant and cools the air before releasing it into the room.
- _____14. If it is not possible to put double pane or low-e glass windows in your home, using solar screens instead of insect screens can greatly reduce summer heat gains.
- _____15. The R-value of low-e double paned windows may be as high as R-3.5. This is higher than regular triple paned windows.
- TEACHER'S NOTES
- Activity 1:
- Possible disadvantages include:
- - Too much bright light and glare let in the house.
- - Too much heat let in the house during the summer.
- - Too much heat escapes through the windows in the winter.
- - Too much air infiltration around windows year-round.
- - Little privacy.
- Activity 2:
- All choices in the left-hand column should be checked:
- - Shade window with trees or shrubs
- - Shade window with roof overhang
- - Use solar screens instead of regular insect screens
- - Use storm windows
- - Put a form of tinting on the outside of the window
- All of these options keep summer heat from ever entering the home. This is more efficient than dealing with the heat once it is in the home. That is what the options in the right-hand column focus on.
- Definitions:
- 1. Heat losses and gains -
- This refers to the loss of desired heat in the winter and the gain of unwanted heat in the summer.
- 2. R-value -
- This refers to a material's resistance to heat. The higher the R-value the better. This means that heat will not be easily conducted through the material.
- 3. Unprotected 1/8" glass -
- This is the most common material used for windows. It is also the most inefficient. Much heat is lost or gained through unprotected glass.
- Answers to Information Check:
- 1. True
- 2. False - Windows are a thermal weak spot since up to 15 times more heat is lost or gained through windows than through an equal area of wall space.
- 3. False - Unprotected glass accounts for about 25% of heat losses in the winter and 25% of heat gains in the summer.
- 4. False - There is much more you can do except have fewer windows. You can use double paned windows, low-e glass, storm windows, plant trees, use solar screens, etc.
- 5. True
- 6. True
- 7. False - Low-e refers to low emittance glass.
- 8. True
- 9. False - A low-e coating on the enclosed surface of the inside pane keeps heat in during the winter. In warm areas like Louisiana where we want to keep heat out in the summer, the coating should be on the enclosed surface of the outer panel.
- 10. True
- 11. False - Low-e windows cost only 10% to 20% more than regular double paned windows.
- 12. False - The gas most used is argon.
- 13. False - Low-e windows with gas use an inert gas because it does not conduct heat as well as air.
- 14. True
- 15. True
Comments or questions to: TechAsmt@LA.GOV
Return to Construction and Design Menu





