What's in the Attic?
- GOAL:
- The student will realize the importance of proper attic ventilation in relation to energy conservation.
- OBJECTIVES:
- The student will be able to:
- 1. State the reasons for using proper attic ventilation.
- 2. Distinguish between a natural gravity venting system and a power driven venting system.
- LESSON / INFORMATION:
- During the hot Louisiana summer, an improperly vented attic can reach up to 160° F. This can increase cooling costs in two ways:
- - Heat and moisture can pass through the ceiling to the air conditioned area below. This causes the unit to work harder as it must cool this infiltrating hot attic air.
- - If the duct work for the air conditioner is located in the attic, heat can pass through the duct walls and into the air being distributed. This causes the unit to distribute warmer air.
- While ceiling insulation and insulation around duct work can help reduce these heat gains, eliminating excess heat from the attic is even more beneficial and cost effective.
- One method of keeping attic heat out of the house below is to use a radiant barrier. A radiant barrier is made of a foil material that reflects radiation up and away from the air conditioned area of the house. This results in less heat gain through the ceiling.
- The amount of heat flow from the attic to the house below is partly dependent on the temperature difference between the two areas.
- Example -
- It is 95°F outside and the house is kept at 78°F. A properly vented attic should only reach about 105°F in this situation, thus creating a 27° temperature difference between attic air and conditioned air.
- An improperly vented attic could reach a temperature of 160°F, thus creating a 82° temperature difference. This would lead to greater conduction of attic heat to the house below.
- To obtain adequate attic ventilation in Louisiana, an air flow of 1.5 cubic feet of air per minute per square foot of attic area is necessary. This can be accomplished by either a gravity venting system or a power driven venting system.
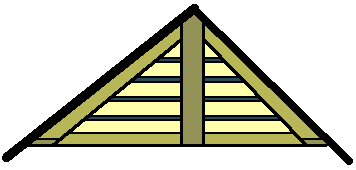
- Gravity vent system -
- To obtain the proper air flow with this natural venting system, a combination of continuous eaves vents and a continuous ridge vent is recommended. The warm air is channeled towards the ridge vent at the peak of the roof where it escapes to the outside. This system moves the most air without the use of electricity.
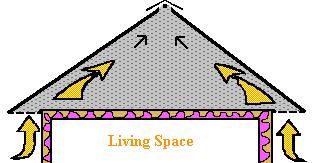
- Another type of natural venting is the turbine outlet vent with continuous eaves vents. The turbines should be located near the ridge of the roof so that wind from any direction will turn them. This will also allow hot air to escape.
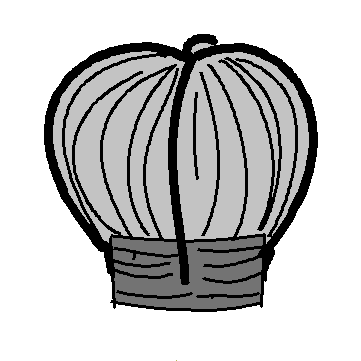
- In Louisiana, this may not work as well as the ridge vent system because there is usually not enough wind to turn the turbines properly.
- Gable vents may be beneficial in cross-ventilation; however, compared to ridge vents, they are not very effective.
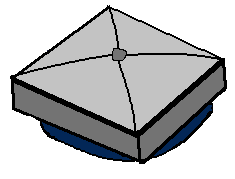
- Power ventilators -
- This is a motor-driven fan that is controlled by a thermostat located around the gable area of the peak of the roof. The thermostat causes the motor-driven ventilator to go on when attic temperature rises. Many experts feel, however, that the cost of powering the electric turbine offsets most savings obtained by cooling the attic.
- FILL IN THE BLANKS:
- 1. The difference in ____ of attic and conditioned air affects heat flow into the house.
- 2. Continuous ____ vents along at least two sides of the house are important in natural ventilation.
- 3. Part of a natural venting system, the _____ is best located near the ridge of the roof.
- 4. Power ____ are motor-driven and help release heat from the attic.
- 5. If an air conditioner ____ is located in the attic, it may cause warmer air to be distributed into the house.
- 6. Ceiling and duct ____ will help reduce heat gains into the house.
- 7. ___ infiltration is a big energy waster.
- 8. The ____ goes along the entire length of the rooftop and is an important part of the gravity vent system.
- 9. A ____ located in the gable area controls the power ventilator.
- 10. A hot attic will leak warm air into the house and cause the ____ to work a lot harder.
- 11. A power ventilator runs on ____.
- 12. The two types of attic ventilation systems are _____ and _______.
- 13. The term ____ refers to a good air flow into and out of the attic.
- 14. The turbine outlet vent may be a problem in Louisiana due to lack of ____.
- 15. Improper venting can cause an ____ to reach 160°F on a hot day.
- RECOMMENDED READING:
- Manual forBuilding Energy Efficient Homes in Louisiana. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources, Baton Rouge, LA, n.d.
- DESIGN ONE Builder's Guide for Energy-Efficient Construction. SLEMCO, Lafayette, LA, 1988.
- INFORMATION CHECK
- Fill in the blanks with words from the following list. Some answers will not be used.
| Ventilation |
|
Heat |
|
Turbines |
| Gravity |
Air ducts |
Wind |
| Vents |
Insulation |
Thermostat |
| Power |
Ridge vent |
Electricity |
| Air conditioner |
Eaves |
Temperature |
| 160°F |
105°F |
125°F |
- 1. When the outside temperature reaches 95°F, a well ventilated attic will reach __________ while a poorly ventilated attic will reach __________.
- 2. The two common ways of venting the attic are with __________ vents or a __________ vent system. Both help to reduce attic temperatures.
- 3. One natural venting system uses __________ placed near the ridge of the roof. In Louisiana, however, they may lack __________ for turning.
- 4. The money saved by cooling the attic with a power vent might be spent on the __________.
- 5. Locating __________ in attics allows heat to warm the air inside them and thus deliver warmer air to the house.
- 6. Warm air infiltration from the attic down into the home causes the __________ to work harder and use more energy.
- 7. Continuous __________ venting and a __________ the length of the roof is recommended as the most
efficient natural venting system.
- 8. Using __________ on the ceiling and around air ducts will reduce heat gain into the house.
- 9. Motor-driven ventilation systems are controlled by a __________ located on or near the roof.
- 10. So what's in the attic during the Louisiana summer? Usually __________!
- TEACHER'S NOTES
- Fill in the Blanks:
- 1. temperature
- 2. eaves
- 3. turbine
- 4. vents
- 5. duct
- 6. insulation
- 7. air
- 8. ridgevent
- 9. thermostat
- 10. airconditioner
- 11. electricity
- 12. power, gravity
- 13. ventilation
- 14. wind
- 15. attic
- Definitions:
- 1. Insulation -
- A material that helps stop the flow of heat.
- 2. Ventilation -
- This refers to adequate air flow in an area.
- Answers to Information Check:
- 1. 105°F, 160°F
- 2. power, gravity
- 3. turbines, wind
- 4. electricity
- 5. air ducts
- 6. air conditioner
- 7. eaves, ridge vent
- 8. insulation
- 9. thermostat
- 10. heat
Comments or questions to: TechAsmt@LA.GOV
Return to Construction and Design Menu







